For online inquiries : bedro1992@goodspine.org
For online inquiries : bedro1992@goodspine.orgAbout Gangnam St.Peter’s General Hospital

Medicine is
science
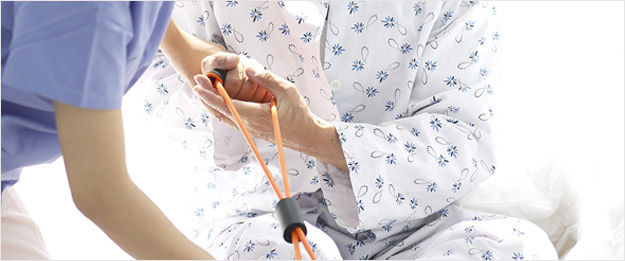
During the early days of our services, the standard diagnostic techniques were not very sophisticated. However, immense progress has been made in both diagnostic and surgical equipment tools in recent years. I have been a grateful beneficiary of this progress. 10 years ago I went through an artificial disc replacement surgery to treat severe lumbar and leg pain.
Inspired by my personal experience, Gangnam St. Peter’s Hospital has adopted the ‘root cause analysis’ approach.
Our methods result in 95% non-surgical and 5% surgical treatments for our patients. To date, we have performed upwards of 4,000 successful artificial disc replacement surgeries.

One Stop
Medical Center
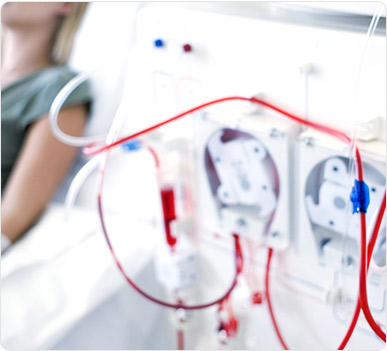
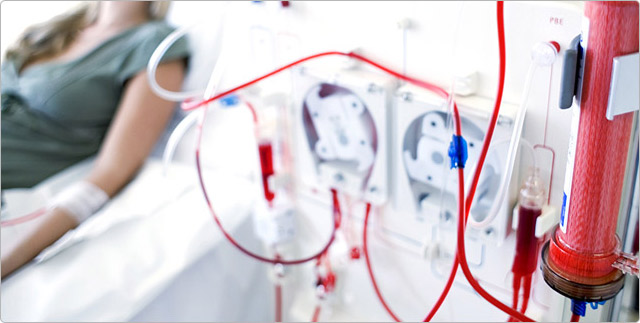
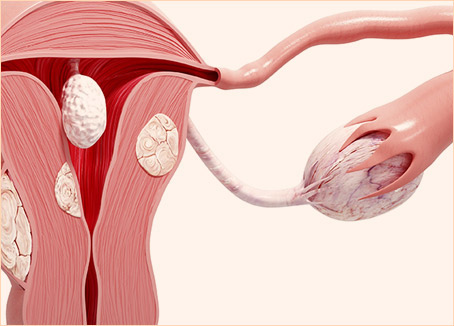
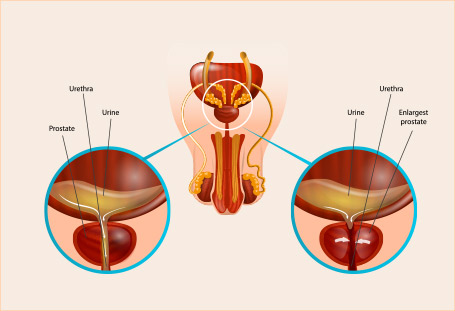
Today, St. Peter's Hospital Gangnam operates a total of 11 departments: Neurosurgical, Orthopedic, Rehabilitation Medicine, Internal Medicine, Cardiology, Nephrology (Dialysis Center), Thyroid Clinic, Urology, Obstetrics & Gynecology, and Physical Examination Center. Our skilled medical team of professionals operates a variety of state-of-the-art machinery (1x 3.0T MRI, 1x 1.5T MRI, 1x 640-channel MDCT high-performance CT scanner) to provide comprehensive, multidisciplinary care on par with any university hospital for our patients. We also offer 24-hour personal assistive care under our combined nursing & caregiving services.

















 Less risk of scarring.
Less risk of scarring. Mammary tissues are
unaffected, causing no
breastfeeding issues.
Mammary tissues are
unaffected, causing no
breastfeeding issues. A safe procedure for
patients having undergone
breast augmentation
plastic surgery.
A safe procedure for
patients having undergone
breast augmentation
plastic surgery. Procedure can be performed
on patients having received
endoscopic surgery previously.
Procedure can be performed
on patients having received
endoscopic surgery previously.